LCN
The LCN integrationIntegrations connect and integrate Home Assistant with your devices, services, and more. [Learn more] for Home Assistant allows you to connect to LCN
Prerequisites
- The integration requires one unused license of the coupling software LCN-PCHK (version >2.8) and an LCN hardware coupler.
- Alternatively, an LCN-VISU or LCN-PKE coupler can be used which offers at least two PCHK licenses. With this setup, sending and receiving commands to and from LCN modules is possible.
The lcn integration allows connections to more than one hardware coupler. For each coupler, a new integration entry needs to be created.
Configuration
To add the LCN integration to your Home Assistant instance, use this My button:
If the above My button doesn’t work, you can also perform the following steps manually:
-
Browse to your Home Assistant instance.
-
In the bottom right corner, select the
Add Integration button. -
From the list, select LCN.
-
Follow the instructions on screen to complete the setup.
Supported device types
There is currently support for the following device types within Home Assistant:
The implemented platforms do not cover the whole functionality of the LCN system.
Therefore the lcn integration offers a variety of events, device triggers and actions.
They are ideal to be used in automation scripts or for the template platforms.
Setting up devices and entites
The lcn hardware modules and groups are represented by Home Assistant devices. The periphery of each lcn module is represented by Home Assistant entities. Peripheries are, for example, the output ports, relays, and variables of a module. Refer to the description of each platform to learn about which entity should be used for which periphery.
The configuration of the lcn devices and entities is completely done using a web user interface (configuration panel).
Once the integration is added to Home Assistant, you can access the lcn configuration panel by selecting the Configure button next to the respective integration entry on the LCN integration page.
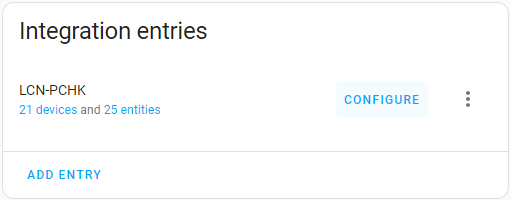
Configuration panel
From the LCN Configuration Panel, you can configure your LCN modules, groups, and entities within Home Assistant.
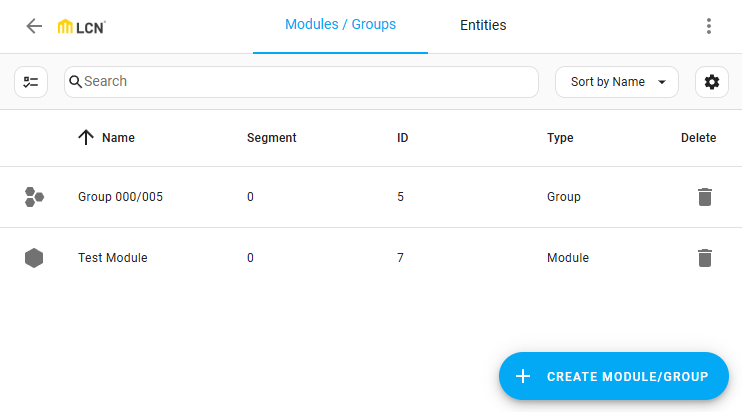
Configuring devices
You can add and remove modules and groups directly from the configuration panel. Once added, they will appear in Home Assistant as devices, which can be used to trigger specific actions within scripts or automations. For examples, refer to the Performing actions page.
The Modules / Groups tab provides an overview of your configured LCN modules and groups, showing their name, ID, and segment ID. The LCN Configuration Panel attempts to derive names from the LCN modules; if a module has no name or is part of a group, a standard name is assigned.
Scanning modules
To initiate a scan for LCN modules on the bus, in the top-right corner, select the three dots
- Result: This process polls each module for its name and serial number.
- When all module responses have been received, they will be listed in the device list.
- Scanning modules may take several seconds. The pop-up dialog will close automatically once the process is complete.
Adding devices
If module scanning fails or a module is unavailable on the bus, you can manually add it. Groups can also be created manually.
-
To add a module or group manually, select the Create Module/Group button.
-
Select whether you want to add a module or group and enter the desired
segment idand module/groupid.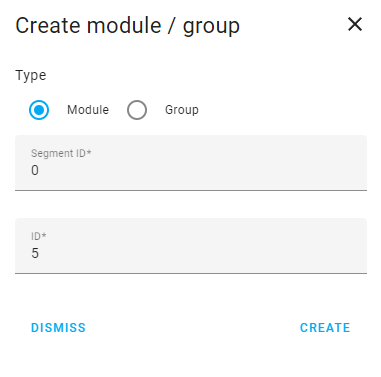
-
To add the new device, select Create.
Deleting devices
To delete a single device, select the trash can icon next to it.
- Result: This will remove the device from the device list and from Home Assistant, including any associated entities.
To delete multiple devices at once, enable selection mode. Select the desired entries, then, in the top-right corner, select Delete Selected.
Configuring entities
Entities configured for all devices are listed on the Entities tab.
To view entities for a specific device (module or group), in the Modules / Groups tab, select the device entry.
- Result: The Entities tab opens, showing entities of the selected device.
- To apply custom filters, enable the filter option.
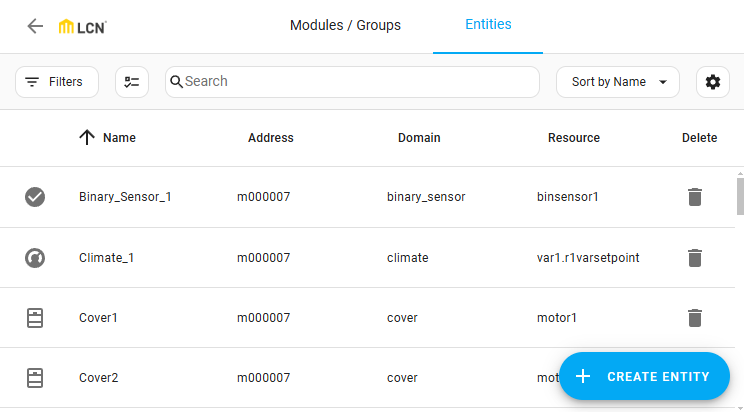
Adding entities
- To create a new entity, select Create Entity.
- From the dropdown menu, select the module or group for which to create the entity.
-
If a single module or group filter is applied, it will be pre-selected.
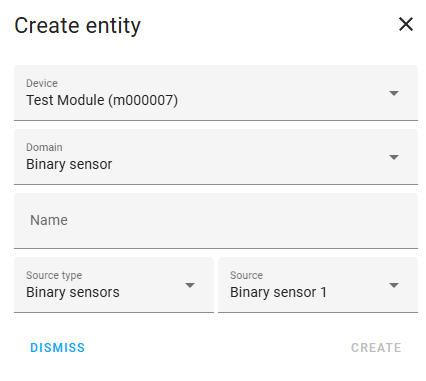
-
- Choose the domain (platform) for the entity and enter a name.
- You can change this name later within the Home Assistant entity settings.
- Depending on the selected domain, additional options will be shown. To add the entity to the list and to Home Assistant, enter the required information and select Create .
Deleting entities
To delete a single entity, select the trash can icon next to it.
- Result: This removes the entity from the list and from Home Assistant.
To delete multiple entities, enable selection mode, select the desired entries, and select Delete Selected in the upper right.
Displaying entity properties
Once an entity is created, you can view and configure its properties.
Select the entity in the entity list.
- This opens the Home Assistant dialog for entity properties, allowing you to configure the entity as you would from the general Home Assistant entity configuration panel.
Platforms
Binary sensor
The lcn binary sensor platform allows the monitoring of the following LCN
- Binary hardware sensors
The binary sensor can be used in automation scripts or in conjunction with template platforms.
Climate
The lcn climate platform allows the control of the LCN
If you intend to leave the regulation to Home Assistant, you should consider using the Generic Thermostat in conjunction with LCN Sensor and LCN Switch.
Cover
The lcn cover platform allows the control of LCN
Only for the module with firmware earlier than 190C:
The configuration allows the optional definition of reverse time. This is the time which is waited during the switching of the motor currents.
The reverse time should only be defined when using the module’s output ports for driving the cover. For all other configuration, the reverse time has to be defined in the LCN Pro software.
For the reverse time, you may choose one of the following constants: RT70 (70ms), RT600 (600ms), RT1200 (1,2s).
If you are using the module’s output ports for motor control, ensure that you have configured the output ports as motor controllers in the LCN Pro software! Otherwise, the output ports are not mutually interlocked and you run the risk of destroying the motor.
Light
The lcn light platform allows the control of the following LCN
- (Dimmable) output ports
- Relays
Scene
The lcn scene platform allows the activation of previously programmed LCN
Sensor
The lcn sensor platform allows the monitoring of the following LCN
- Variables
- Regulator setpoints
- Thresholds
- S0 inputs
- LED states
- Logic operation states
The sensor can be used in automation scripts or in conjunction with template platforms.
Ensure that the LCN module is configured properly to provide the requested value. Otherwise, the module might show unexpected behavior or return error messages.
Switch
The lcn switch platform allows the control of the following LCN
- Output ports
- Relays
- Lock state of regulators
- Lock state of keys
Additional features
Transponder, fingerprint sensor and code lock
To use LCN transponders, fingerprint sensors or code locks ensure that the corresponding module’s I-port property is enabled in the LCN-PRO software and properly configured. LCN transponders, fingerprints and code locks are identified by a six value hexadecimal code (e.g. 123abc). If a code is received a corresponding event (transponder event, fingerprint event, codelock event) is fired and can be used to trigger an automation. Alternatively, you can use the corresponding device triggers.
Example:
This example shows how the event_data can be extracted and used in a condition using Home Assistant’s templating engine.
Trigger on a transponder event and ensure that the received code is in the given list:
automation:
triggers:
- trigger: event
event_type: lcn_transponder
conditions: "{{ trigger.event.data.code in ['aabbcc', 'ddeeff', '112233'] }}"
actions:
...
Further examples can be found in the event section.
Remote control
To use LCN remote controls (e.g., LCN-RT or LCN-RT16) ensure that the corresponding module’s I-port property is enabled in the LCN-PRO software and its behavior is properly configured as “IR access control”. With this configuration each remote control is identified by a six value hexadecimal code (e.g. 123abc). If a command from a remote control is received a corresponding event (transponder event) is fired and can be used to trigger an automation. Along with the transmitted code, the pressed key and the key action are transmitted. Alternatively, you can use the corresponding device triggers.
Examples can be found in the event section.
LCN commands addressed to PCHK host (Home Assistant)
A LCN module can not only be programmed to send commands to other modules/groups but also to the PCHK host configured in the LCN integration. These commands are directly passed to Home Assistant and can be evaluated. Only the send keys (former) command is supported.
Within LCN-PRO program the send keys command (only “A-C former command” is supported) to a key. For the target address manually enter the PCHK host id (default: 4). Select the keys and key actions as desired.
When a send keys command is received, the LCN integration will fire a send keys event for each key configured. These events can be used to trigger an automation. Alternatively, you can use the corresponding device triggers.
Examples can be found in the event section.
Only commands sent from physical buttons of a module are evaluated. The “Test command” button in the LCN-PRO software is not evaluated and therefore cannot be used for testing purposes.
Events
There are several functionalities of the LCN system which are not exposed as regular entities by the integration, but as events. Examples are button presses from remote controls (transmitters), transponder findings, fingerprint sensors and so called send keys events.
If you find it difficult to deal with events in scripted automations, you can also use device triggers which offer automation design via the UI.
All events have some common attributes in their event_data which identify the sending LCN hardware module (e.g., the module the transponder is connected to):
| Event payload | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
device_id |
Internal device id of LCN module | string |
segment_id |
Module’s segment id | 5..128 |
module_id |
Module id | 5..254 |
In addition, every event has its own special attributes which are described below. All special attributes are optional and can be used as supplementary filters.
Event: lcn_transmitter
The lcn_transmitter event is fired if a LCN remote control command is received.
| Special payload | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
code |
Transmitter code | string (6 hex values) |
level |
Key level | 0..4 |
key |
Key | 0..4 |
action |
Key action |
hit, make, break
|
Example:
The trigger will fire if any key on the remote control with code 123abc is hit as long as the
receiver hardware is connected to module 7 in segment 0.
automation:
triggers:
- trigger: event
event_type: lcn_transmitter
event_data:
segment_id: 0
module_id: 7
code: 123abc
action: hit
Event: lcn_transponder
The lcn_transponder event is fired if a LCN transponder command is received.
| Special payload | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
code |
Transponder code | string (6 hex values) |
Example:
The trigger will fire if the transponder with code 123abc was detected at any hardware module.
automation:
triggers:
- trigger: event
event_type: lcn_transponder
event_data:
code: 123abc
Event: lcn_fingerprint
The lcn_fingerprint event is fired if a LCN fingerprint command is received.
| Special payload | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
code |
Fingerprint code | string (6 hex values) |
Example:
The trigger will fire if the fingerprint with code 123abc was detected at any hardware module.
automation:
triggers:
- trigger: event
event_type: lcn_fingerprint
event_data:
code: 123abc
Event: lcn_codelock
The lcn_codelock event is fired if a LCN code lock command is received.
| Special payload | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
code |
Code lock code | string (6 hex values) |
Example:
The trigger will fire if the code lock with code 123abc was activated at any hardware module.
automation:
triggers:
- trigger: event
event_type: lcn_codelock
event_data:
code: 123abc
Event: lcn_send_keys
The lcn_send_keys event is fired if the PCHK host receives a send keys command.
| Special payload | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
key |
LCN Key | a1..c8 |
action |
Key action |
hit, make, break
|
Example:
The trigger will fire if the PCHK host receives a command that issues a hit of
key a1.
automation:
triggers:
- trigger: event
event_type: lcn_send_keys
event_data:
key: a1
action: hit
Device triggers
To simplify using events in automations the LCN integration exposes them as device triggers. Those device triggers can be selected from the automation editor within Home Assistant.
After creating a new automation select Device as trigger type and search for the module which is supposed to cause the event in the device list. You may select the trigger type and configure its attributes. If an attribute is optional it is considered as a supplementary filter for the trigger. For an explanation of the attributes refer to the corresponding events.
Actions
In order to directly interact with the LCN system, and invoke commands which are not covered by the implemented platforms, the following actions can be used. Refer to the Performing actions page for examples on how to use them.
Action: output_abs
Set absolute brightness of output port in percent.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
output |
No | Output port of module | OUTPUT_PORT |
brightness |
Yes | Absolute brightness in percent | 0..100 |
transition |
Yes | Transition (ramp) time in seconds | 0..486 |
Example:
action: lcn.output_abs
data:
address: myhome.0.7
output: output1
brightness: 100
transition: 0
Action: output_rel
Set relative brightness of output port in percent.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
output |
No | Output port of module | OUTPUT_PORT |
brightness |
Yes | Relative brightness in percent | -100..100 |
transition |
Yes | Transition (ramp) time in seconds | 0..486 |
Example:
action: lcn.output_rel
data:
address: myhome.0.7
output: output1
brightness: 30
Action: output_toggle
Toggle output port.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
output |
No | Output port of module | OUTPUT_PORT |
transition |
Yes | Transition (ramp) time in seconds | 0..486 |
Example:
action: lcn.output_toggle
data:
address: myhome.0.7
output: output1
transition: 0
Action: relays
Set the relays status. The relays states are defined as a string with eight characters. Each character represents the state change of a relay (1=on, 0=off, t=toggle, -=nochange).
Example states: t---001-
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
state |
No | Relay states as string |
Example:
action: lcn.relays
data:
address: myhome.0.7
state: t---001-
Action: led
Set the LED status.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
state |
No | LED state as string | LED_STATE |
Example:
action: lcn.led
data:
address: myhome.0.7
led: led6
state: blink
Action: var_abs
Set the absolute value of a variable or setpoint.
If value is not defined, it is assumed to be 0.
If unit_of_measurement is not defined, it is assumed to be native.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
variable |
No | Variable name | VARIABLE, SETPOINT |
value |
Yes | Variable value | any positive number |
unit_of_measurement |
Yes | Variable unit | VAR_UNIT |
Example:
action: lcn.var_abs
data:
address: myhome.0.7
variable: var1
value: 75
unit_of_measurement: %
Ensure that the LCN module is configured properly to provide access to the defined variable. Otherwise the module might show unexpected behaviors or return error messages.
Action: var_rel
Set the relative value of a variable or setpoint.
If value is not defined, it is assumed to be 0.
If unit_of_measurement is not defined, it is assumed to be native.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
variable |
No | Variable name | VARIABLE, SETPOINT, THRESHOLD |
value |
Yes | Variable value | any positive or negative number |
unit_of_measurement |
Yes | Variable unit | VAR_UNIT |
Example:
action: lcn.var_rel
data:
address: myhome.0.7
variable: var1
value: 10
unit_of_measurement: %
Ensure that the LCN module is configured properly to provide access to the defined variable. Otherwise the module might show unexpected behavior or return error messages.
Action: var_reset
Reset value of variable or setpoint.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
variable |
No | Variable name | VARIABLE, SETPOINT |
Example:
action: lcn.var_reset
data:
address: myhome.0.7
variable: var1
Ensure that the LCN module is configured properly to provide access to the defined variable. Otherwise the module might show unexpected behavior or return error messages.
Action: lock_regulator
Locks a regulator setpoint.
If state is not defined, it is assumed to be False.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
setpoint |
No | Setpoint name | SETPOINT |
state |
Yes | Lock state | true, false |
Example:
action: lcn.lock_regulator
data:
address: myhome.0.7
setpoint: r1varsetpoint
state: true
Action: send_keys
Send keys (which executes bound commands).
The keys attribute is a string with one or more key identifiers. Example: a1a5d8
If state is not defined, it is assumed to be hit.
The command allows the sending of keys immediately or deferred. For a deferred sending the attributes time and time_unit have to be specified. For deferred sending, the only key state allowed is hit.
If time_unit is not defined, it is assumed to be seconds.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
keys |
No | Keys string | |
state |
Yes | Keys state | KEY_STATE |
time |
Yes | Deferred time | 0.. |
time_unit |
Yes | Time unit | TIME_UNIT |
Examples:
Send keys immediately:
action: lcn.send_keys
data:
address: myhome.0.7
keys: a1a5d8
state: hit
Send keys deferred:
action: lcn.send_keys
data:
address: myhome.0.7
keys: a1a5d8
time: 5
time_unit: s
Action: lock_keys
Locks keys.
If the table is not defined, it is assumed to be table a.
The key lock states are defined as a string with eight characters. Each character represents the state change of a key lock (1=on, 0=off, t=toggle, -=nochange).
The command allows the locking of keys for a specified time period. For a time period, the attributes time and time_unit have to be specified. For a time period, only table a is allowed.
If time_unit is not defined, it is assumed to be seconds.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
table |
Yes | Table with keys to lock | |
state |
No | Key lock states as string | KEY_STATE |
time |
Yes | Time period to lock | 0.. |
time_unit |
Yes | Time unit | TIME_UNIT |
Examples:
Lock keys forever:
action: lcn.lock_keys
data:
address: myhome.0.7
table: a
state: 1---t0--
Lock keys for a specified time period:
action: lcn.lock_keys
data:
address: myhome.0.7
state: 1---t0--
time: 10
time_unit: s
Action: dyn_text
Send dynamic text to LCN-GTxD displays. The displays support four rows for text messages. Each row can be set independently and can store up to 60 characters (encoded in UTF-8).
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
row |
No | Text row 1..4 | |
text |
No | Text to send for the specified row |
Example:
action: lcn.dyn_text
data:
address: myhome.0.7
row: 1
text: "text in row 1"
Action: pck
Send arbitrary PCK command. Only the command part of the PCK command has to be specified in the pck string.
| Data attribute | Optional | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
address |
No | LCN address | |
pck |
No | PCK command |
Example:
action: lcn.pck
data:
address: myhome.0.7
pck: PIN4
LCN constants
The actions use several predefined constants as parameters.
Ports
| Constant | Values |
|---|---|
| OUTPUT_PORT |
output1, output2, output3, output4
|
Motors
The motor values specify which hardware relay or outputs configuration will be used:
| Motor | Relay on/off | Relay up/down |
|---|---|---|
motor1 |
relay1 |
relay2 |
motor2 |
relay3 |
relay4 |
motor3 |
relay5 |
relay6 |
motor4 |
relay7 |
relay8 |
| Motor | Output up | Output down |
|---|---|---|
outputs |
output1 |
output2 |
Variables and units
| Constant | Values |
|---|---|
| VARIABLE |
var1, var2, var3, var4, var5, var6, var7, var8, var9, var10, var11, var12, tvar, r1var, r2var
|
| SETPOINT |
r1varsetpoint, r2varsetpoint
|
| THRESHOLD |
thrs1, thrs2, thrs3, thrs4, thrs5, thrs2_1, thrs2_2, thrs2_3, thrs2_4, thrs3_1, thrs3_2, thrs3_3, thrs3_4, thrs4_1, thrs4_2, thrs4_3, thrs4_4
|
| VAR_UNIT |
native, °C, °K, °F, lux_t, lux_i, m/s, %, ppm, volt, ampere, degree
|
| TIME_UNIT |
seconds, minutes, hours, days
|
States
| Constant | Values |
|---|---|
| LED_STATE |
on, off, blink, flicker
|
| KEY_STATE |
hit, make, break, dontsend
|
Keys
Whenever a key has to be provided, it is defined by a joint string consisting of the table identifier (a, b, c, d) and the corresponding key number.
Examples: a1, a5, d8.